Task management is an important part of managing the Raspberry Pi. This is more difficult on the Raspberry Pi than on a normal computer because it is run in headless mode. This means that the Raspberry Pi is being controlled remotely by another computer. Instead of opening a task manager on the Raspberry Pi, the following instructions state a better way to manage tasks.
Starting a Script in the Terminal
Although scripts can be executed (run) in many ways, the simplest and easiest way to run scripts is the terminal. For this project, you will be running Python in the terminal.
Install Python 3 on your computer. On Linux machines, this can be done by opening a terminal and running
sudo apt install python3
To run your code, go to the directory of the Python script and run
python3 python_script.py
This would run the file
python_script.pyin the terminal. On some computers, usually computers where Python 2 is not installed, you can replacepython3withpythonin the command, but this is guaranteed to work.If you want to debug your code, it may be advantageous to run the command with a
-iflag. This means that a Python console will open after the program is executed, where one can access variables and other data. Run this by writing the following command:python3 -i python_script.py
To exit the Python console, use the shortcut
CTRL+dor runquit()in the console.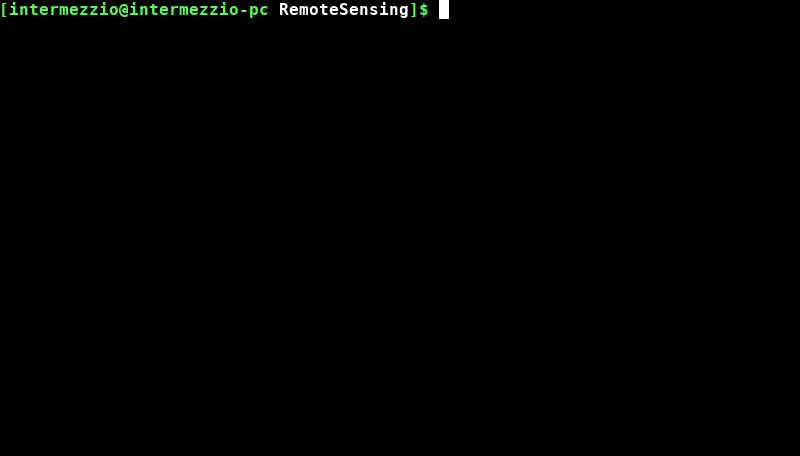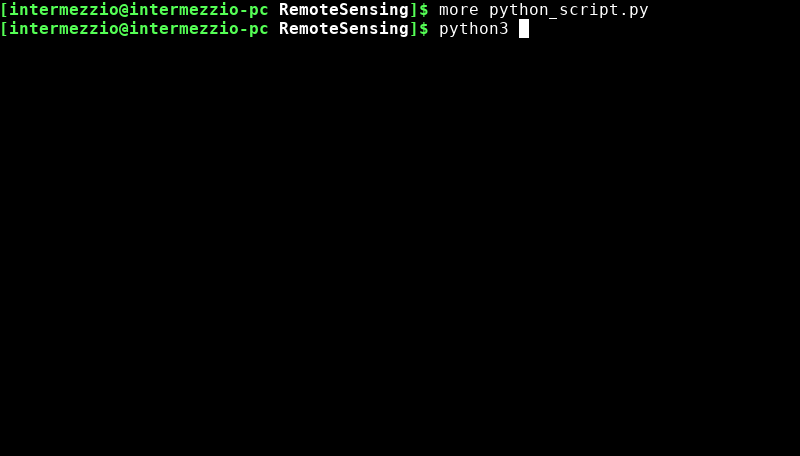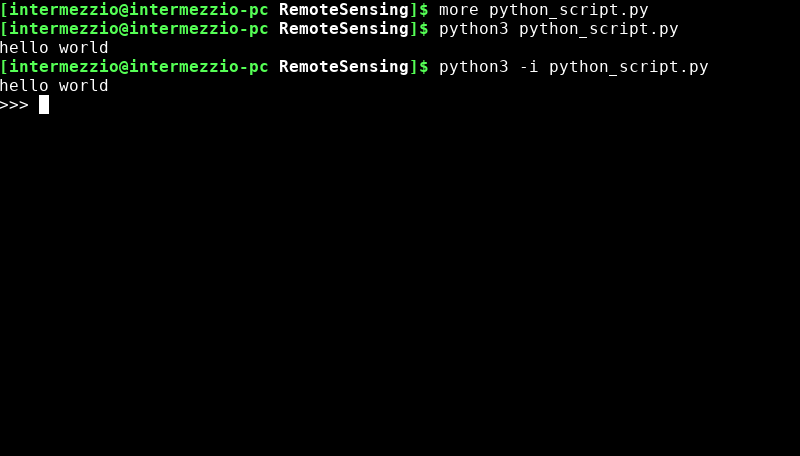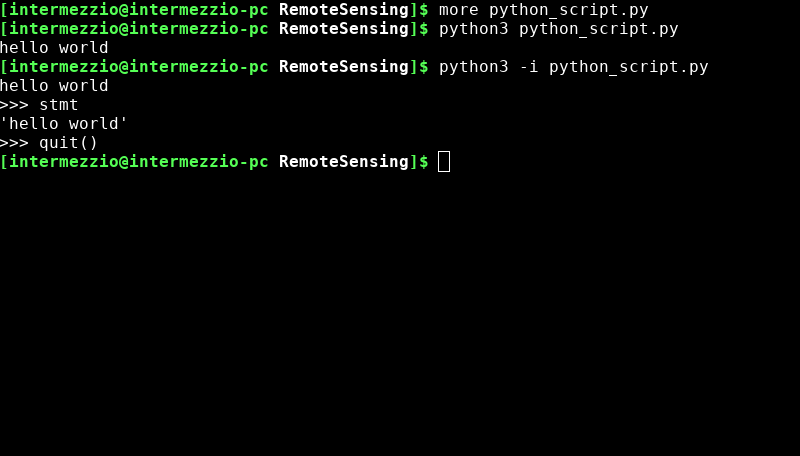
Ending a Script Using the Task Manager
A task manager is important for remotely managing your scripts on the Raspberry Pi. Because the Raspberry Pi has a weak processor, it is ideal to use a terminal based task manager to end unnecessary tasks, like scripts that have already completed.
After you SSH into the raspberry pi, open a terminal and write
ps aux
This will list all of the tasks running on the Raspberry Pi.
To search for a specific task (like a script), use the
grepfeature. The following line shows how you can search for all tasks with the name “python in them.ps aux | grep python
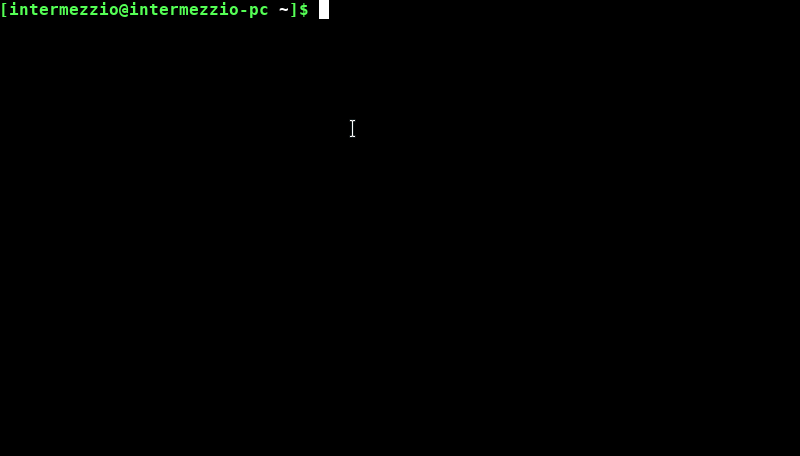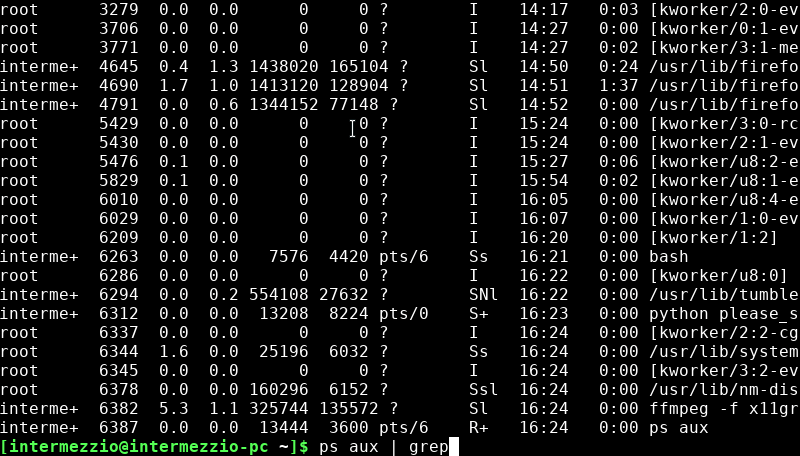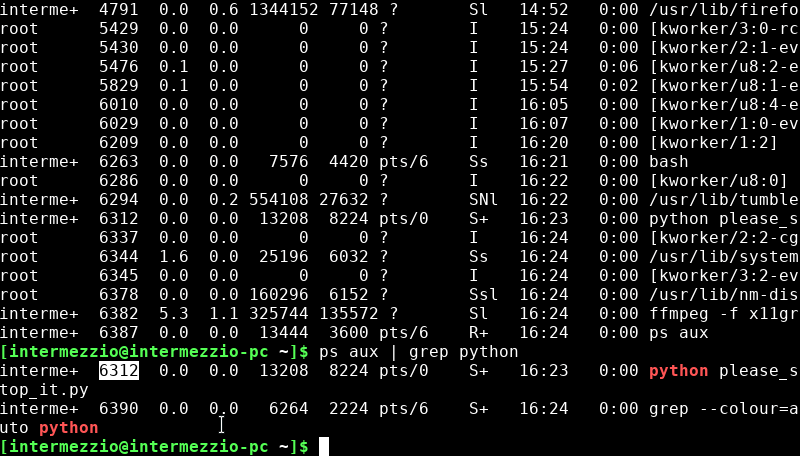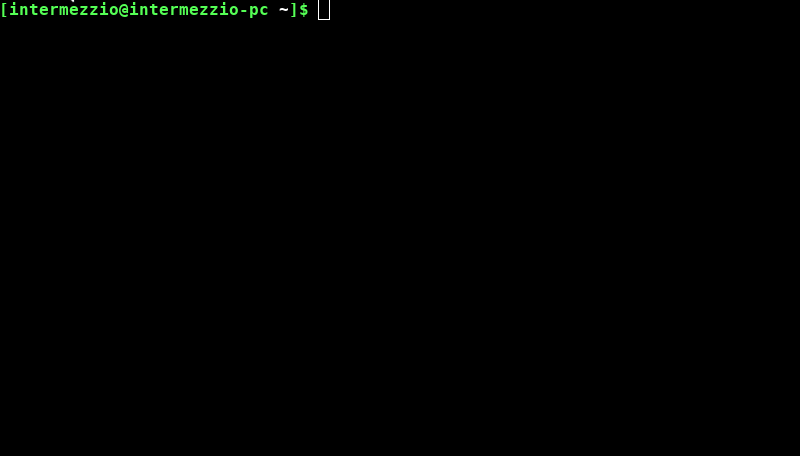
The pipe (“|”) tells the computer to take the output of
ps auxand search for it using grep. The output of this function may look like the following:interme+ 6632 0.2 0.0 13208 8436 pts/0 S+ 16:30 0:00 python please_stop_it.py interme+ 6635 0.0 0.0 6264 2348 pts/6 S+ 16:30 0:00 grep --colour=auto python
Please Note: There are two tasks in the output that have the name ‘python’ in it. The first one (
6632) is the command forpython please_stop_it.py, and the task that needs to end. However, the second command isgrep python, or the command running right now to search in the task manager. Killing this process is useless and does not affect the python script.Once you’ve found the task, take the id of the task (a four digit number on the same line as the task name) and run the following code:
kill [####]
This ends that task. The following example involves opening the task manager and ending a task for a Python script.